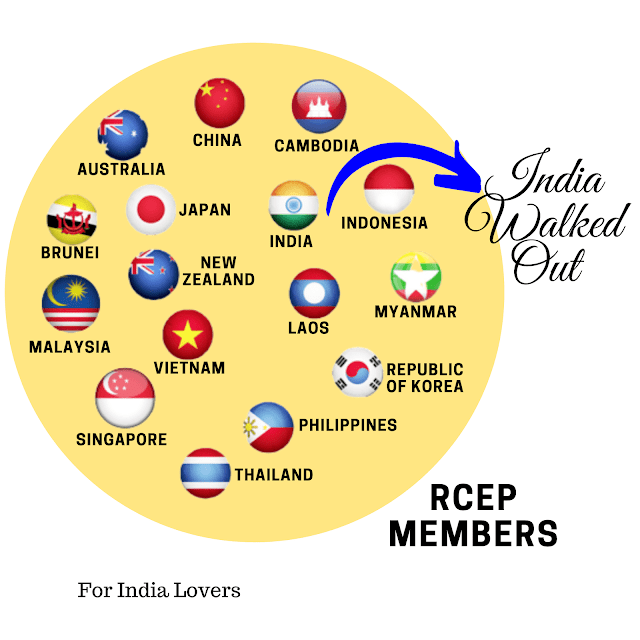
RCEP Agreement: India decided to Withdraw from Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership
This article talks about the RCEP agreement which is regional comprehensive economic partnership, its origin and purpose. It also discusses about the reasons behind the decision of India to withdraw from this agreement and what will be the impact of this decision on India and other member countries.
Introduction
Origin of RCEP Agreement
Stand of India
Concerns of India
Demands of India
Impact of Withdrawal of India on RCEP Members
Future Course
Conclusion
Introduction
RCEP agreement (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership) is an attempt to become the largest trading block of the world which encompasses 30% of global GDP, 25% of global trade and 50% of global population. It was a proposed free trade agreement to be conciliating among sixteen countries to promote the free flow of goods and services in Asia Pacific region. The proposed sixteen member countries were ten ASEAN countries and six other countries namely India, China, South Korea, Japan, Australia and New Zealand. ASEAN countries are Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, Cambodia, Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines, Brunei and Singapore.
Origin of RCEP Agreement
The free trade agreement called regional comprehensive economic partnership (RCEP) was initiated by China to counter the influence of USA led TPP (Trans Pacific Partnership). It was initiated in 2012 by Beijing. Though it was initiated by China but built around ASEAN countries. The objective was to increase the trade among Asia Pacific region.
Stand of India
Since beginning of this initiative, India has put forward its concerns about the RCEP agreement (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership). Even after long discussions, concerns of India were not addressed. That is why in 3rd RCEP summit which was held in November 2019 in Bangkok, government of India made clear its stand by withdrawing from RCEP agreement in order to protect national interests.
Concerns of India
Though RCEP agreement (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership) increases the market access for the member countries but there are some issues for which India is concerned. These issues are described below:
- India is very much concerned about flooding of Indian market with the cheap Chinese products. Due to lack of freedom to impose anti dumping duty if bound under RCEP agreement, India will not be able to protect the domestic manufacturers.
- Under the pact of regional comprehensive economic partnership, India is not getting adequate market access in service sector.
- There is no provision in RCEP agreement about assurance on “Rules of Origin”. As per the agreement, lesser rates of tariff would be required to impose on ASEAN countries than China by India. Indian concern is that China could circumvent rules of origin by selling their products to India through ASEAN countries.
- The base year 2014 is also a concern for India because it could lead to lowering of tariff rates and impact badly on local manufacturers. With this base year, duties on electronic products will fall to almost zero.
- India is already facing huge trade deficit with China which is almost USD 50 - 53 bn. The overall trade with all the proposed signatories of RCEP is a worth of USD 105 bn.
- If Indian market is opened by signing RCEP (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership), it could be harmful to farmers also especially those involved in milk production due to import of low cost milk from other countries like New Zealand.
Demands of India
In the light of above concerns, India tried to seek following from the discussions and negotiations on RCEP agreement:
- An operation is required to stop surge of imports. It may be rise of duties in case of sudden flooding of market.
- Dairy sector, auto industries and certain textiles should be kept out of this pact.
- Strict investment regime and dispute management operation should be made available.
- Strict norms about origin of product are required to curb the abuse of free trade agreement.
- India proposed base year to be 2019 rather than 2014.
Impact of Withdrawal of India on RCEP Members
Decision of India will impact all the member countries of RCEP (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership). The countries like Australia and New Zealand are producers of primary products like milk. They need large market of India. ASEAN countries also want inclusion of India in RCEP agreement so that they can make a balance with China and prevent its dominance. China itself needs more access to Indian market for which it was pushing hard so as to compensate its loss due to ongoing trade war with USA.
Future Course
India has a target to make Indian exports (merchandise goods and services) of USD 1 trillion by 2024. To achieve this target required growth rate cannot be achieved just by service sector. India needs to accelerate its growth rate by making it a manufacturing hub. Its competitiveness is required to increase in a globalized world. Indian market should be opened gradually. A high level advisory group set up by commerce minister submitted its report in which it emphasized on cost of capital, labour reforms and change mindset.
Conclusion
Though withdrawal of India from RCEP will keep India out of the benefits of this pact but the decision taken on the basis of assessment of current global situation, Indian competitiveness, fairness and balance of the agreement is justified. The doors are not closed forever. It is hope that future negotiations may be in favour of India. By the time, India should make a time bound reform program and follow it strictly.
See Other Posts: Indian Economy Slowdown, Agricultural Problems in India


No comments