DNA Study of Skeleton at Rakhigarhi, Indus Valley Civilization – Depicting New Facts about Past of Indians
This article talks about findings of a genetic study of DNA from the skeleton of a woman found at Rakhigarhi, a well known site of Indus Valley Civilization. To make one better understand about the research findings, a brief about past beliefs are discussed. It also discusses how the research findings have enough potential to rewrite the history of North Indians by debunking the existing beliefs.
Indus Valley Civilization
Aryan Theory
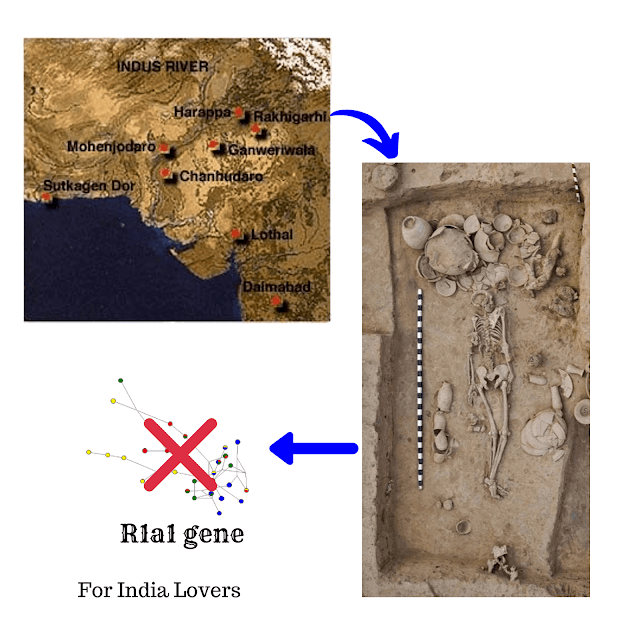
Rakhigarhi
Threats to Rakhigarhi
Research about Rakhigarhi
Findings of Research
Conclusion
Indus Valley Civilization
Indus Valley Civilzation (IVC) was a grand urban civilization settled in the region of present North Western India and whole Pakistan. The major sites of Indus Valley Civilzation are Harrappa and Mohanjodaro. The first discovered IVC site was Harappa, which is located in present day Pakistan. On the name of this site, Indus valley civilization is also called as Harappa Civilization. Other sites found in India are Lothal, Dholavira, Rakhigarhi, Banawali etc.
Aryan Theory
In early 20th century, historians put forward a theory called Aryan Invasion Theory. The theory proposed that Aryans invaded in South Asia. They defeated the natives of Indus valley civilization and conquered the territory. They established a new settlement, which was rural one. That period is known as Vedic era.
By the end of 20th century, most of the historians negated Aryan Invasion Theory and replaced it with Aryan Migration Theory. Their new belief was the Aryans did not invade. Rather they migrated in to Indian subcontinent from Eurasian Steppes and the areas of Mesopotamia and Anatolia (present Turkey). The migrants from Eurasian steppes were pastoralists and those from Mesopotamia and Anatolia were farmers. Some also believed that Aryans came from Arctic region. Thus, proponents of this theory advocate that Aryans brought with them practices of farming and cattle rearing. They also introduced their language which further developed group of Indo-European languages.
Rakhigarhi
Rakhigarhi is a small village located in Hansi Tehsil of Hisar district in Haryana. It was considered as a small site of Indus valley Civilization. It is one of few IVC sites found in North India. It is located on the plains of Ghaggar-Hakra river. Excavation at this site started in 1960s. In 2014, several new settlements were found at this site in a necropolis. Now, Archaeologists do not consider it a small site. It has become the largest site of Indus Valley Civilization, even larger than Mohandodaro. Now, it is believed that this site may even extend from 80 Ha to 550 Ha
Threats to Rakhigarhi
The threats faced by Rakhigarhi include encroachment by villagers and stealing of artifacts by locals. In 2012, Global Heritage Fund declared it as one of the ten most endangered heritage sites in Asia. Since this site is a village and villagers cultivate the land here, people do not want to leave their houses and fields. Thus, it is difficult for Archaeological Survey of India to continue the excavation by displacing the local people.
Excavation at Rakhigarhi
This site is believed to be a pre-Indus valley settlement because its existence dates back to 6500 BCE. It is also a mature Indus valley site back to the period of 2600-1900 BCE. The excavation at this site discovered seven mounds and several other settlements in the vicinity. Mounds formed due to deposition of soil and other territorial content on the settlements of Indus Valley.
Research about Rakhigarhi
Rakhigarhi is a site of attraction of archaeologists. A research paper about Rakhigarhi has published in a journal “Cell”. This study was conducted on DNA of a woman skeleton found at Rakhigarhi. It was conducted by renowned archaeologist Vasant Shinde. He is vice-chancellor at Deccan College, Pune. The project was conducted in collaboration with CCMB (Center for Cellular and Molecular Biology) Hyderabad, Harvard Medical College and Birbal Sahni Institue of Paleobotany, Lucknow. The study is about gene sequencing.
Findings of Research
- The breakthrough finding of DNA analysis is the absence of R1a1 gene which is believed to be known as “Aryan Gene” in India. This finding suggests that inhabitants Indus Valley Civilization were not same as Aryans.
- Indus valley settlers had distinct genetic lineage. The DNA found in the skeleton matches with that of Andaman’s tribes and ancient Iranians.
- Though the research publication itself directly does not claims rejection of “Aryan Migration Theory” but the results indicate that the Aryan Theory stands refuted.
- The hunters and gatherers settled in Harappa and Indus valley were present even before arrival of new settlers from Eurasia and Anatolia (present day Turkey).
- Evidences were also found which suggest east to west migration from the sites located in Turkmenistan and Iran.
- In this research, no evidence was found to support large scale migration of people in to South Asia before pastoralists arrived from European Steppes and introduced Indo-European languages in to Indian subcontinent nearly 4000 years ago.
- Population of Indian subcontinent was heterogeneous right from the beginning of settled life.
- Farming and animal domestication travelled from South Asia to West Asia not vice versa. Few migrations from West Asia to South Asia were due to trade relations.
Conclusion
The latest research evidence supports distinct genetic lineage of original inhabitants of Indus valley civilization. Their ancestry is different from migrants from steppe pastoralists and Iranian farmers. The new evidences suggest that Harappans were themselves Aryans. No Aryan migration took place. Small scale migration of Steppes pastoralists and Iranians occurred only due to trade relations. The research proves a serious blow to Aryan Theory.
See Other Posts: Paika Rebellion, 1857 Revolt



No comments