Chief of Defence Staff – New Position for Better Coordination of Armed Forces of India
This article talks about the origin of a new position called “Chief of Defence Staff”. It also discusses the need of this position, its roles and responsibilities, first CDS of India. It also hints about history of all three defense forces of India which are Indian Army, Indian Navy and Indian Air Force.
Background
Origin of Chief of Defence Staff
First Chief of Defence Staff of India
Chief of Defence Staff
Role of Chief of Defence Staff
Indian Army
Indian Air Force
Indian Navy
Conclusion
Background
Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) has its origin in the roots of Kargil war 1999. The idea of CDS arose almost 2 decades back. The war of Kargil between India and Pakistan questioned the coordination among the armed forces of India during critical times. A review committee was set up to review the whole Kargil war. Subramanyam Committee recommended the creation of position of CDS (Chief of Defence Staff). In 2012, another committee headed by Naresh Chandra recommended for the position of Chief of Staff Committee (COSC). Till now, the senior most chief among all the three armed forces used to act as the chairman of COSC but its tenure had short duration and it was an additional responsibility.
Origin of Chief of Defence Staff
During celebrations of Independence Day of India in 2019, Prime Minister Sh. Narendra Modi declared the position of Chief of Defence Staff. The position got approval on 24th December 2019 by Cabinet Committee on Security. The idea mooted by Kargil review committee got implemented in the year 2019.
First Chief of Defence Staff of India
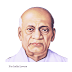
The first CDS of India is General Bipin Rawat who was also Chief of Indian Army for three years. General Bipin Rawat is senior most chief among all the three chiefs of armed forces. He joined the position of CDS on 31st December 2019. He is fit for the position of Chief of Defence Staff.
Past Experience of General Bipin Rawat
Mr. Rawat handled various operational duties in Line of Control, Line of Actual Control and North East of India. He has experience of conducting operations in high altitude, difficult terrains and also in disturbed areas. General Bipin Rawat is honored with many bravery awards in his service of 39 years. He was rewarded with “Sword of Honor” also. He led infantry battalion in eastern sector in Line of Actual Control, National rifles sector and infantry division in Kashmir valley. He was also Colonel military secretary in Military secretary’s branch. He also acted as Logistic officer in Central India division. He was appointed as Chief of Indian Army in 2016 and joined this position on 31st December 2016.
Educational Background
Mr. Bipin Rawat did his initial schooling from St. Edward’s School Shimla. He was also a student of NDA Khadakwasla. He completed his graduation from Defence Services Staff College, Wellington. General Bipin Rawat is M. Phil in defense studies from Madras University. He is also Ph.D. from Chaudhary Charan Singh University, Meerut. He did research on military media strategic studies. General Rawat wrote several articles on national defence and leadership.
Chief of Defence Staff
The position of Chief of Defence Staff is created with the purpose of bringing all the defence forces of India under one umbrella to achieve appropriate coordination among them. It is designed in a way to prevent power concentration in one person. That is why CDS (Chief of Defence Staff) is a 4 star officer. It is not given a rank of 5 star. Similar positions exist in other countries like Great Britain, United States of America, China, Italy, France, Canada, Japan etc. Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) will not directly lead three armed forces. Rather, he will seek advice from respective chiefs of three defence forces. The position is immune from political influence so that CDS can take military decisions without any bias.
Role of Chief of Defence Staff
Office of Chief of Defence Staff is located in South block. It is above all the three defence forces of country. The roles and responsibilities of CDS are discussed below:
- Chief of Defence Staff will act as chief advisor to Ministry of Defence in all matters related to defence. The new position will act as a single point of contact between defence ministry and defence forces.
- He will act as secretary of Department of Millitary Affairs, a new department created under Ministry of Defence.
- Chief of Defence Staff is also a member of DAC (Defence Acquisition Council) and that of Defense Planning Committee.
- In addition to giving strategic advice to defence ministry, CDS will be involved in long term planning of national defence.
- His role is coordination of all three defence forces, creation of strong network among them and better management of military resources.
- All defence purchases, training and recruitment of defence forces will be subjected to the scanning by Chief of Defence Staff.
- The new position of CDS is going to take directly under its ambit all the tri-services organizations. Such tri-services organizations are Andaman & Nicobar command, Integrated Theater command, Strategic forces which deal with missiles, nuclear assets; and other tri-services organizations dealing in cyber security, space and special forces.
- The tasks of Chief of Defence Staff (CDS)are development of uniform thinking in all the defence forces, reorganization of armed commands, development of joint commands when needed etc.
- Apart from above, CDS has to engage in promotion of use of indigenous armed equipments.
Indian Army
Indian Army is the second largest standing army of the world. It had its origin in British colonial times in India. British Indian Army was organized by East India Company. Initially this force comprised armies of three presidencies. During Second World War, this force was converted to British Indian Army. Later, after Indian Independence, armed forces of princely states were also integrated in to it. On 15th January 1949, Indian Army came in to existence. Lieutenant General K.M. Cariappa was the first who occupied the position of commander in chief of Indian Army. Every year, 15th January is celebrated as Army Day of India. Indian Army is an all voluntary force. About 80% of active defence personnel in India are engaged in Indian Army. It is designed as regiment system. It is divided in to seven commands on the basis of basic territorial division, operational and geographical lines.
Objectives of Indian Army
The objectives of Indian Army are:
- To ensure national security and promotion of national unity
- Protection of India from external aggression and internal threats
- Maintenance of peace and order
- Saving lives during natural disasters and management of disasters
Indian Air Force
Indian Air Force ranks fourth among all air forces of the world. It was formerly known as Royal Indian Air Force. Indian Air Force was officially formed on 8th October 1932. It flew its first flight on 1st April 1933. Initially it had only one contingent and only 19 air force personnel. In 1939, when Japanese used air force, Royal Indian Air Force was subjected to expansion. Before Indian freedom, Indian Air Force could appoint 1600 officers. On 15th August 1947, property of Indian Air Force was divided between Indian and Pakistan.
Indian Air Force has seven commands out of which five are operational and two are functional. The five operational commands are Western, Eastern, Central, Southern and South Western which have their headquarters in Delhi, Shillong, Allahabad, Thiruvananthapauram and Gandhi Nagar respectively. At present, Indian Air Force have 20 helicopter units, 45 wing squadrons, 1700 aircrafts and 1, 20,000 personnel.
Indian Navy
Indian Navy is the oldest of all the three defence forces of India. In was used organized by British East India Company in 1612. In 1686, it was called “Bombay Marine”. In 1830, it was renamed as “Her Majesty Indian Navy”. Later, in 1892, this force became “Royal Indian Marine”. In 1934, “Royal Indian Navy” came in existence under Indian Naval (Discipline) Act 1934. Indian Naval Force had only 8 warships in the beginning of Second World War. Now, Indian Navy has aircraft carrier INS Vikramaditya, Nuclear ballistic missile submarine INS Arihant. It has 14 frigates, 11 destroyers, 24 fighter ships, 29 guard ships, 2 nuclear marines, 13 other submarines and many other naval vessels.
Conclusion
The national security is not only based on military actions. Diplomacy is equally important. Overall military diplomacy is a part of foreign policy of India. If India wants to create its space globally especially in Asia Pacific region, it needs to bring coordination in defence, finance and external affairs. Hopefully, new position of Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) will prove its potential in optimizing and regulating necessary military and administrative actions.
See Other Posts: Special Protection Group, Police Reforms in India



No comments