Ebola Virus Disease - An Outbreak Declared as Public Health Emergency
This article talks about spread of ebola virus disease, ebola outbreak and the action taken by international community to tackle it. It also discusses its ebola symptoms, diagnosis and ebola treatment. What are the hurdles to control this disease and how it can be controlled?
Introduction to Ebola Virus Disease
Ebola Outbreak
Structure and Replication of Ebola Virus
Spreas of Ebola Virus
Types of Ebola Virus
Ebola Symptoms
Ebola Diagnosis
Ebola Treatment
WHO Stand
Causes of Failure to Combat Ebola Virus Disease
Introduction to Ebola Virus Disease
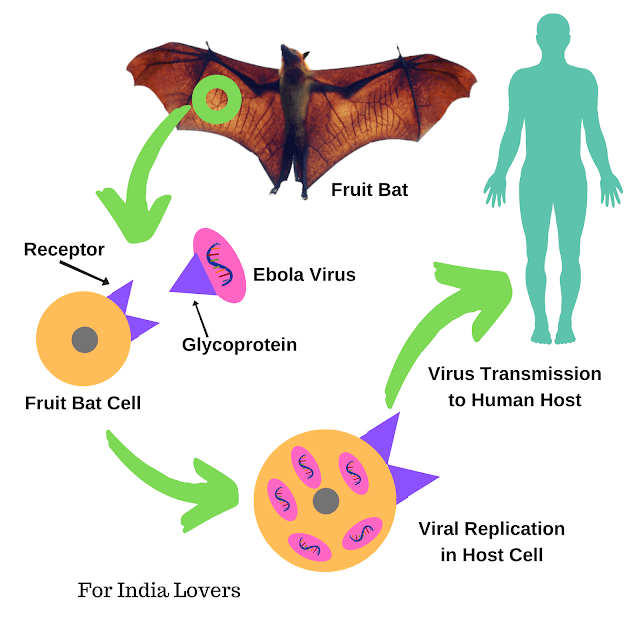
Ebola virus disease or Ebola haemorrhagic fever is a zoonotic disease caused by virus. The responsible virus is an RNA virus which was first time detected in 1976 in Africa. The vector carrying viruses is primarily fruit bat. Other vectors are monkey, ape, chimpanzee, gorilla and porcupine.
Ebola Outbreak
Since its first detection in 1976, first ebola outbreak occurred in 2014 which lasted till 2016. This is called first phase of ebola outbreak when it was spread in four countries of Africa and they were Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia and Nigeria. More than 11000 people got killed in the first phase. The second phase started in 2018 in Democratic Republic of Congo which is still going on.
Structure and Replication of Virus
Ebola virus is composed of a proteinaceous sac enclosing nucleoprotein. The outer coat carries glycoproteins which are recognized by the target cells of virus. After being recognized by target cell, ebola virus enters in the host cell and uses its machinery for translating proteins. In other words, target cell gets simply hijacked by virus and used by virus to replicate itself. The resulting ebola viruses attack other host cells.
This viral infection of ebola also spreads to other animals if they come in direct contact of the infected one or through the bodily secretions like faeces, blood, vomit, urine, saliva, semen or other fluids like nasal or ocular discharges. The infected animal spreads the infection to other animals and also humans. Then, further human to human transmission occurs.
Type of Ebola Viruses
There are five species of ebola virus:
- Zaire Ebola Virus (EBOV)
- Bundibugyo Ebola Virus (BDBV)
- Sudan Ebola Virus (SUDV)
- Tai Forest Ebola Virus (TAFV)
- Reston Ebola Virus (RESTV)
Ebola Symptoms
Ebola is a fatal disease. Its mortality rate can be as high as 90%. Ebola symptoms may become visible in 8 – 10 days though incubation period is between 2 – 21 days. The ebola symptoms are fever, inflammation, headache, sore throat, muscle pain, abdominal pain, and rashes. Later stages may develop other symptoms of vomiting, diarrhoea, impaired kidney functions, fall in WBCs count and platelet count, internal and external bleeding, and impaired liver functions.
Ebola Diagnosis
Ebola virus disease can be diagnosed by ELISA, Antigen recognition test, PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) assay.
Ebola Treatment
- Since there is no cure available for ebola, the best possible option is its prevention.
- The infected person should be immediately isolated to prevent the infection.
- Patient should be given supportive care like giving fluids and maintaining electrolyte balance.
- Protective wears should be worn by those taking care of patients.
- Precautions should also be taken by those visiting hospitals.
- Visits to infected area should be avoided.
- Even contact with the dead bodies of infected people can cause infection. So be cautious.
- The susceptible people should be vaccinated. During first outbreak, no was available. But this time two vaccines are available which are VSV- EBOV and rVSV – ZEBV.
WHO Stand
WHO declared ebola outbreak in DRC as a public health emergency. This is fifth time that such declaration is done by WHO.
Causes of Failure to Combat Ebola Virus Disease
- Reluctance in community and lack of cooperation
- Attack on health workers
- Delays in case detection and isolation
- Lack of financial aid.
If appropriate steps are not taken at right time, ebola can take a toll of hundreds of lives. International community is taking suitable steps and persuading G-7 countries to give the financial support as committed by them.
See Other Posts: Conservation of Tigers in India, Maternal Mortality Ratio Declining in India



No comments